Priority Rules Overview
How to Navigate: Click on Planning > Planning Rules Config > Plant Calendar
Summary
The priority rules screen provides users with a way to define rules and rulesets that will directly tell the planning system how it should make decisions when creating a production schedule. The typical workflow of this screen is that users will start on the Rules Search tab. This tab presents users with a data grid where each row is a rule. The name and description columns are both user defined fields that can be used to give a sense of what the rule does at a glance. The active column indicates whether the rule will be ignored or applied by the planning system.
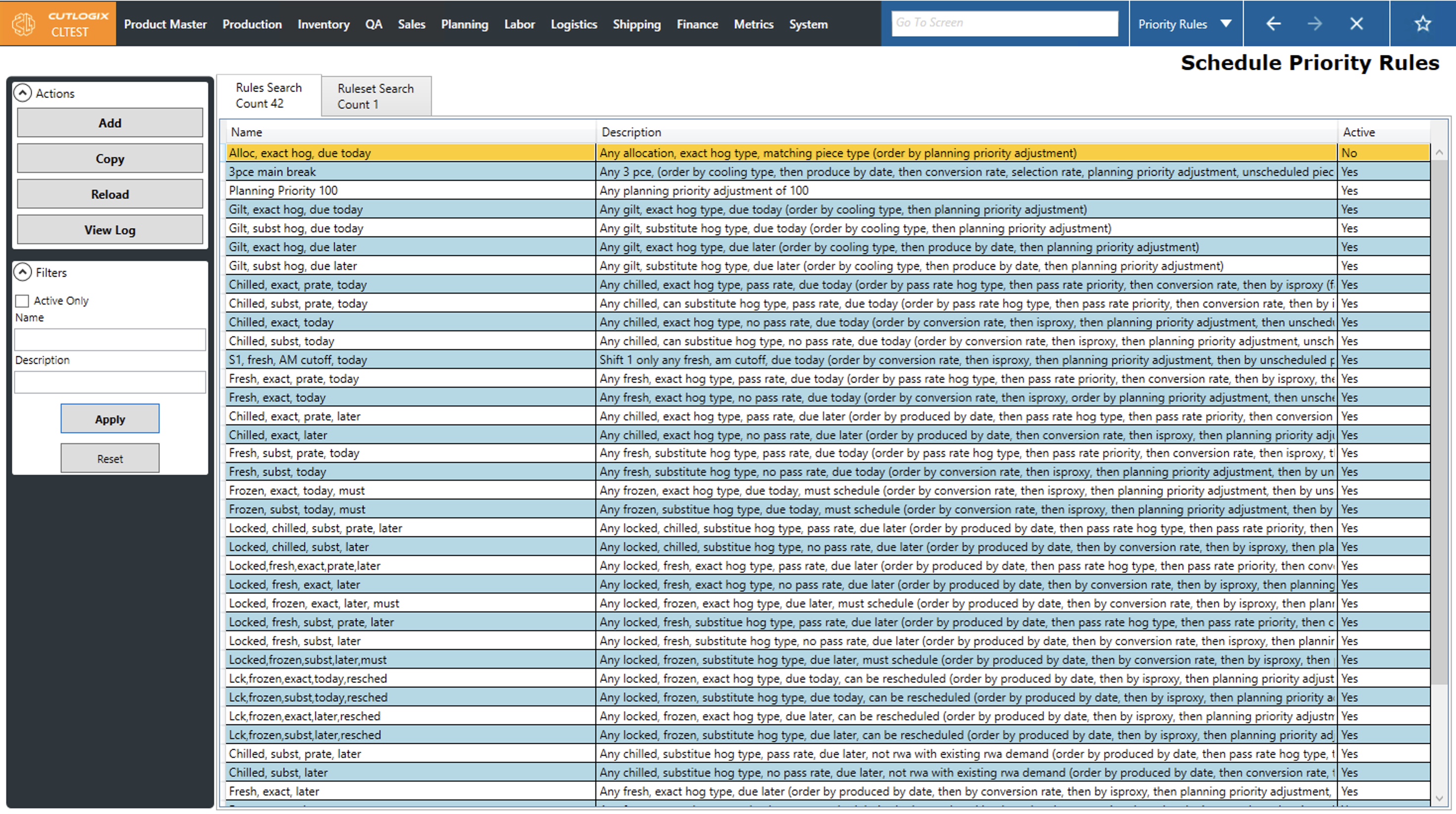
When users create rules on the Rules Search tab, they are added to the pool of available rules that can be added to rulesets on the Ruleset Search tab.
When users add rules to rulesets, they can use the UI to move created rules from the Available Rules section over to the Active rules that are part of the set. Rules are defined to match different types of demand. When rules are placed into the Active Rules section, the order of the rules tells the planning system which types of demand should be scheduled first, second, third, etc in line with the priority column.
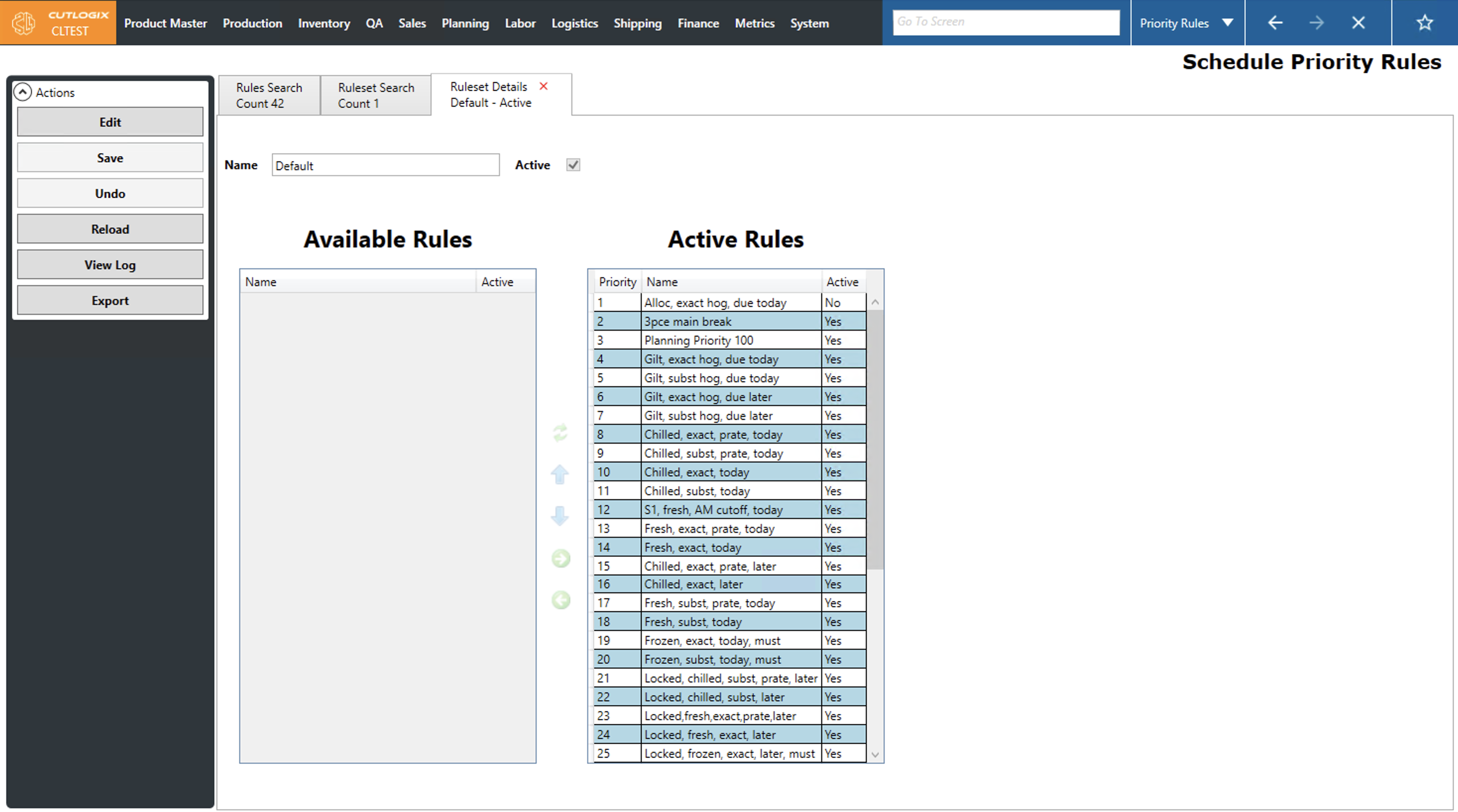
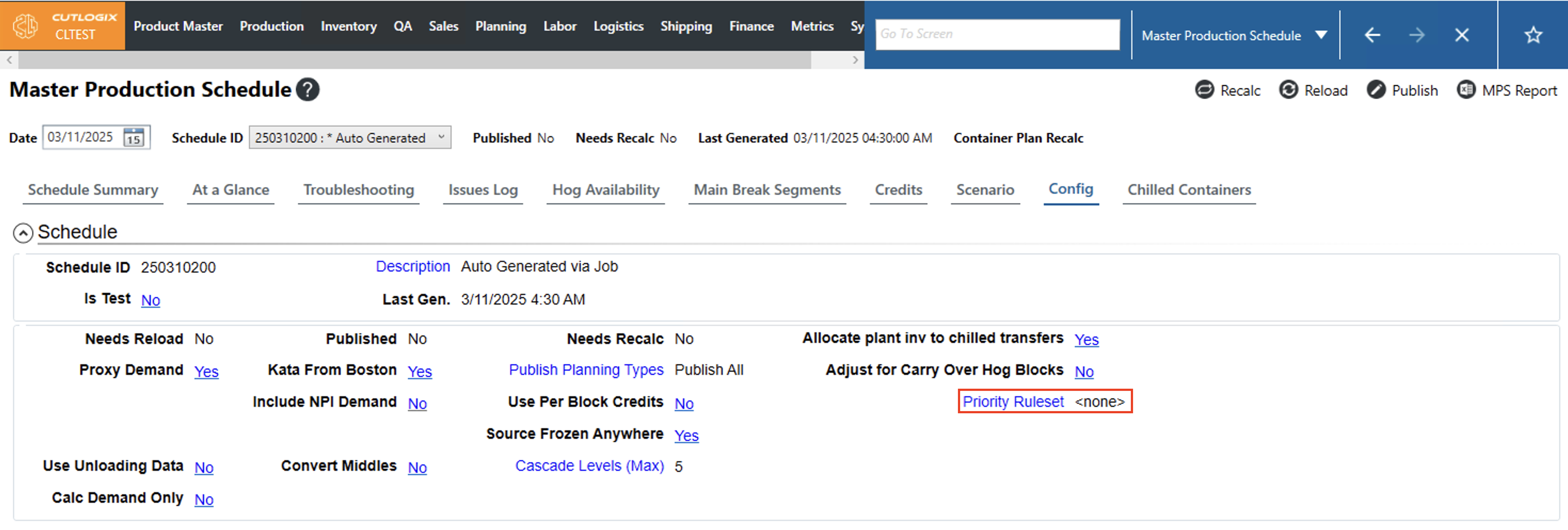
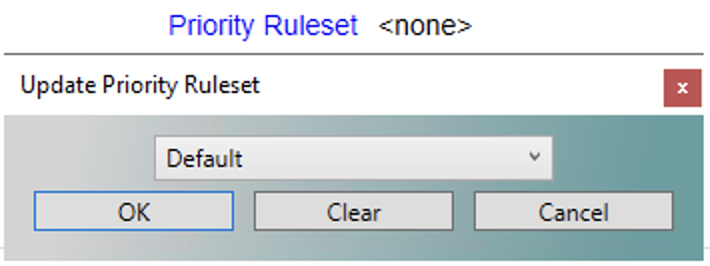
Once a ruleset has been created, users can assign it to a schedule in the MPS on the config tab. If the 'none' option is selected then the system will default to a set of hardcoded rules. Clicking the hyperlinked text will allow users to select a defined ruleset from the dropdown and click ok to apply it to the selected schedule.
Matching Criteria Options
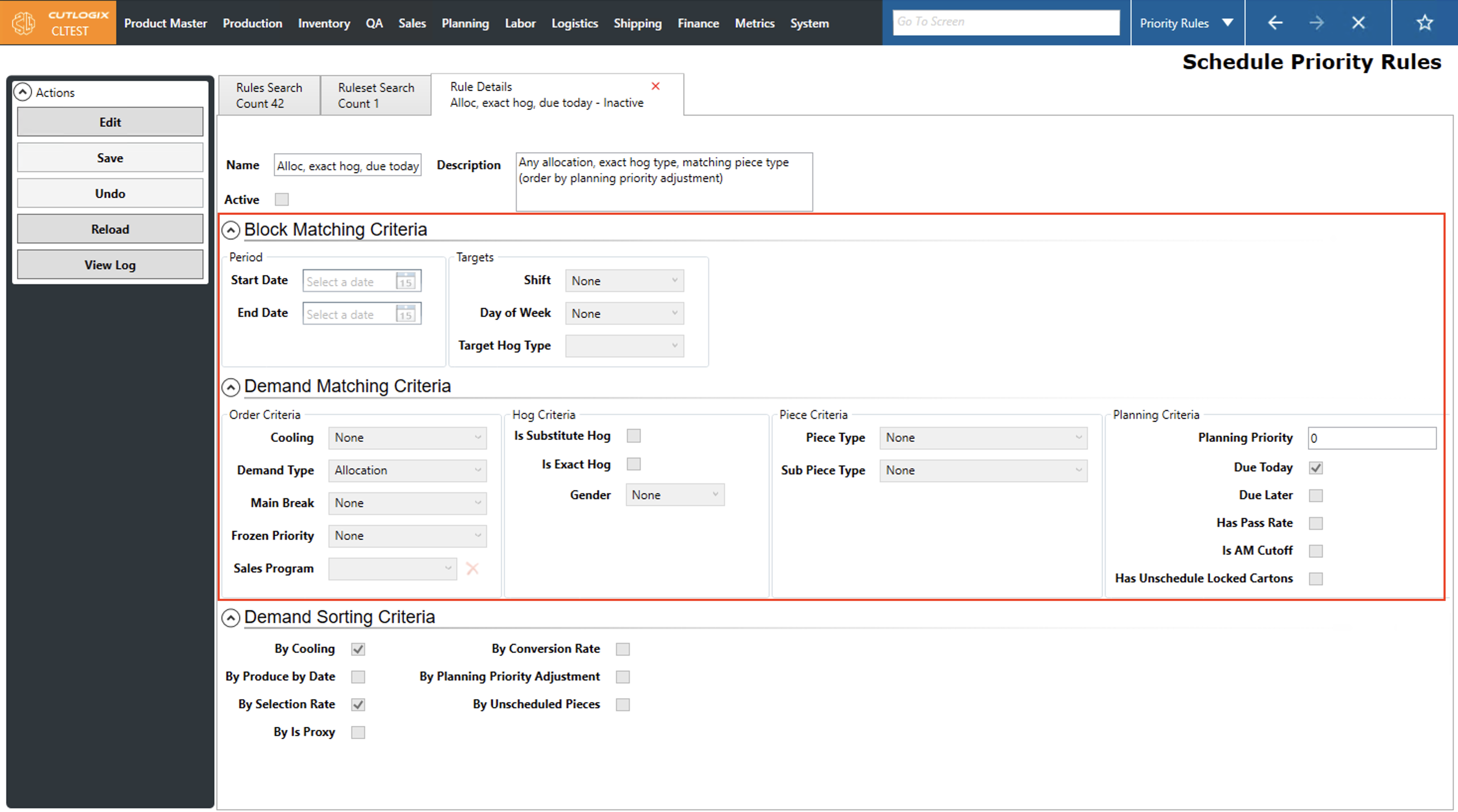
User defined priority rules have two parts. The first is the matching criteria as defined in the Block Matching Criteria and the Demand Matching Criteria sections of the rule’s details tab. This criteria is used by the planning system to determine which demand meets this rule.
Rule Details
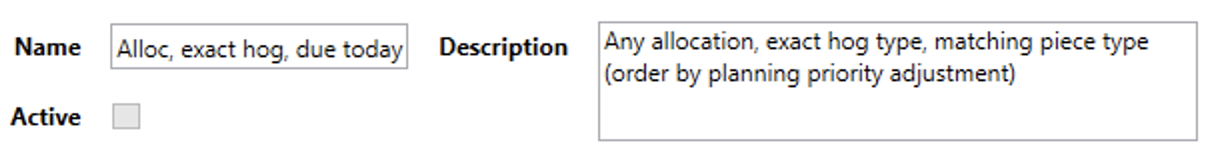
- Name - Users can define a succinct name that captures the rule’s function at a glance.
- Description - Users can provide a more detailed explanation of what enabling this rule will tell the planning system to do.
- Active - If a rule is active, it will be applied by the planning system when added to an active ruleset. If it is not active, it can still be added to a ruleset but the planning system will ignore it.
Block Matching Criteria
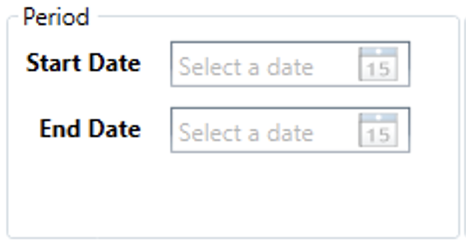
Period
- Start/End Date - If users want the rule to only be in effect temporarily, then can use these fields to define its effective date range.
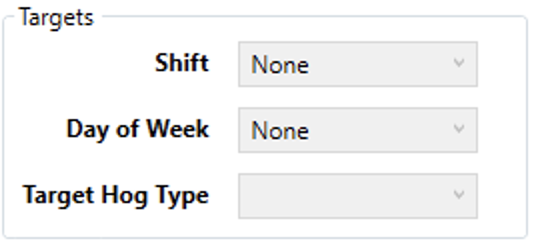
Targets
- Shift - Defines which shift the rule will apply to.
- Day of Week - Defines the day of the week the rule will apply to.
- Target Hog Type - Defines the specific type, or grade, of hog the rule should apply to. Hog types/grades refer to the type of breeding program and diet the hogs underwent. Typically, the more stringent the program the more expensive the hog.
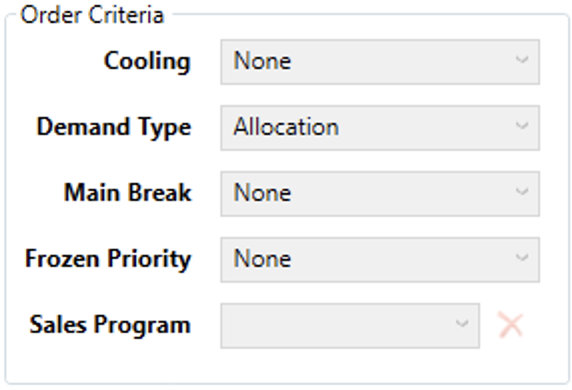
Demand Matching Criteria
Order Criteria
- Cooling - Choose the product cooling type the rule will apply to.
- Fresh - Product that is typically produced and shipped the same day. It is kept and shipped at cool temperatures but above frozen and chilled.
- Frozen - Product that is produced and then placed in a freezer until completely frozen. It is kept and shipped at temperatures below freezing.
- Chilled - Product that is produced and then placed in a cooler to chill it down to temperatures just above 0℃ to extend its shelf life without freezing it. It is kept and shipped at those temperatures.
- Demand Type - Defines the type of demand that the rule will apply to
- None - Default value that means the rule shouldn’t apply to a demand type.
- Allocation - This is demand that is allocated toward a production agreement. For example, a customer may ask for a set number of pieces over the next few weeks but may not commit to ordering it. The planning system will forecast a plan for it, i.e. allocation generic production to it, but will only actually include this demand in the final production plan if the customer puts in a formal order for it.
- Default - Demand generated to produce a production default.
- Locked Production Order - This is demand where the production of a certain product is locked at a set quantity for certain day and shift.
- Manual - Demand created by a user entering a manual production order. These are created on the Manual Production Orders screen.
- Mid shift - Demand created by the addition of a mid-shift adjustment. These are created on the Manual Production Orders screen.
- Order - Demand generated by a customer order.
- Proxy - Demand generated from an order for a product that must be derived from the production of another product.
- Reservation - Demand generated by a Sales Reservation.
- Scenario - Demand generated by an override input on the Scenario tab in the MPS.
- Main Break - Chooses the type of main break that the rule should apply to. Main Break refers to how the carcass is initially split at the start of processing.
- Frozen Priority - Chooses whether the rule should affect products with certain frozen priorities. Frozen priorities are either ‘Can Reschedule’ or ‘Must Schedule’ which tells the planning system whether it can bump frozen production to make room in the schedule for something else.
- Sales Program - Choose which Sales Program the rule should apply to. Sales Programs are defined on Sales > Sales Programs. They are a way of tagging certain products as being a part of a certain sales initiative.
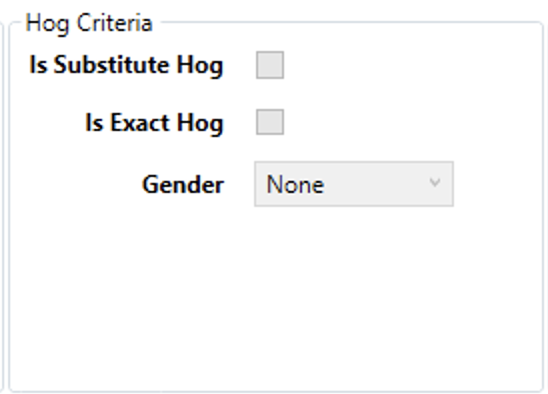
Hog Criteria
- Is Substitute Hog - Indicates that the rule should apply to demand that allows the chosen hog type to be substituted for a hog type of equal or greater quality..
- Is Exact Hog - The rule should apply to demand that require a specific hog type with no substitutions allowed.
- Gender - Determines whether the rule will apply to demand with a specific gender.
- Barrow - Castrated male hogs.
- Gilt - Female hogs that either have not had a litter or have been bred specifically for slaughter.
- Mixed - Allows any gender to be used for production.
Piece Criteria
- Piece Type - Specify the piece type to which the rule should apply. These typically refer to primal or subprimal pieces.
- Sub Piece Type - Specify a subpiece type to which the rule should apply. These typically refer to cuts that are derived from primal or subprimal pieces.
Planning Criteria
- Planning Priority - Choose the demand’s planning priority that the rule should apply to. The lower the number the higher the priority.
- Due Today/Later - Can specify if the rule should apply to demand that is being produced on the current day or on a future day.
- Has Pass Rate - Determines if the rule should apply to products that have a pass rate. Specifically, this refers to products with a pass rate of less than 100% that necessitates scheduling production for the pieces that do not pass.
- Is AM Cutoff - Determines if the rule should apply to demand that must be produced in the AM on the day it is scheduled.
- Has Unschedule Locked Cartons - This demand record has locked cartons, i.e. cartons with a manual maximum on the current day and shift, that are unscheduled.
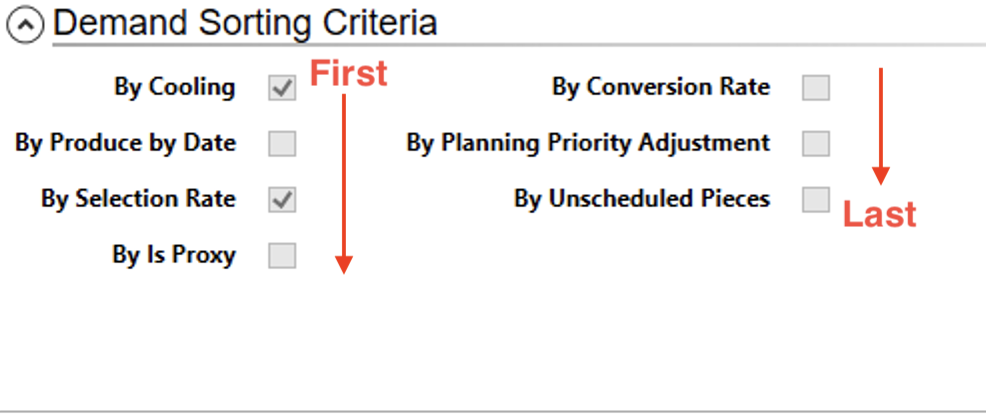
Sorting Criteria Options
The second part of a priority rule is the sorting criteria, i.e. the criteria that helps the planning system to break ties and sort the multiple demand records that may meet the matching criteria. Checking one of the boxes tells the planning system to use that sorting criteria, unchecking tells it to ignore it. Each of these criteria are applied based on the order they appear in the list. Furthermore, each are applied in ascending order, i.e. dates go from old to new, numbers go from smallest to largest and words go into alphabetical order.